Key words:AKI (Acute Kidney Injury), Cardiorenal Syndrome
ROC analysis of 14-day mortality rate
In March 2012, the KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury guideline related to the treatment of AKI (Acute Kidney Injury) was published by the KDIGO (Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes) foundation which was established with the aim of developing international guidelines for kidney disease[1]. In this publication, although serum creatinine level and urine volume are always defined as conventional AKI criteria, the overestimation of AKI diagnose performance and the necessity of biomarkers which are able to diagnose AKI in early stage were pointed out, due to low production of creatinine in ICU patients with sepsis induced AKI.
Before that a new biomarker started to be practiced in medical field, this index has to assure the approved standard level of diagnostic accuracy determined by each country’s authority. Among biomarkers which the clinical evaluation has been advanced internationally in recent years, those approved by or applying for FDA in US, CE marking in EU and Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan as an IVD products, are listed as below:
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin(NGAL)
Cystatin C
Interleukin 18(IL-18)
Kidney injury molecule-1(KIM-1)
L-type fatty acid binding protein(L-FABP)
The English review article[2] that adopts these 5 items as the so-called five biomarkers of AKI is introduced in the above-mentioned KDIGO guidelines.
Below is an example showing the clinical data comparing the diagnosis performance of above biomarkers in Japan.
Method
The urinary biomarkers such as L-FABP, NGAL, NAG, albumin, and serum creatinine in 339 mixed ICU admitted critically ill adult patients, was measured at their admission and the performance of these biomarkers was determined using ROC curve analysis for 14-day mortality.
Results
The urinary levels of L-FABP and other biomarkers such as NAG, albumin, NGAL and IL-18, of 339 ICU patients were measured and compared. Among the 274 patients who have no AKI at the ICU admission, 66 have developed AKI within one week. The level of different biomarker at admission were also compared in order to see the performance and consequently, it reveals that urinary L-FABP has the best early diagnosis performance.
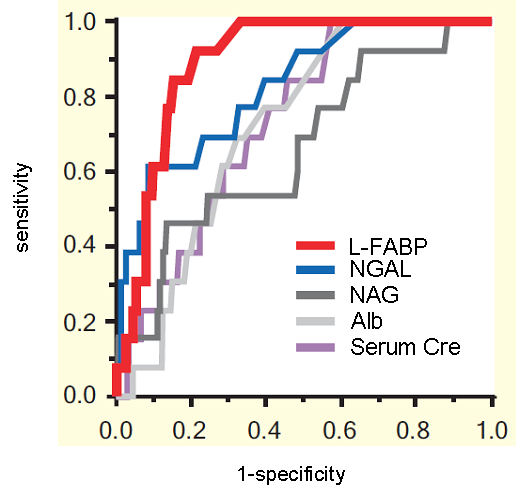
(partially modified from figure 3 of article [3])
Furthermore, several urinary biomarkers level at the time of ICU admission were measured and compared and the prediction of mortality rate of all 339 cases within two weeks after admission, was assessed. In result, urinary L-FABP had very high precision, with an ROC area under curve of 0.90, which shows high diagnosis performance and this was significantly superior compared to NAG and albumin (Table).
*Among 339 patients, 14 (4.1%) died within 2 weeks after mixed ICU admission.
| ROC Area Under Curve (AUC-ROC) | |
| L-FABP | 0.896 |
| NGAL | 0.827 |
| NAG | 0.664 |
| Albumin | 0.717 |
| Serum creatinine | 0.733 |
Above result shows that urinary L-FABP is able to determine with high degree of accuracy, the mortality prediction in drug-induced nephropathy, sepsis and multi-organ failure patients at their mixed ICU admission.
References
- [1] KDIGO(Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes) http://www.kdigo.org/clinical_practice_guidelines/AKI.php
- [2] Moore, E., et al., Biomarkers of acute kidney injury in anesthesia, intensive care and major surgery: from the bench to clinical research to clinical practice. Minerva Anestesiol. 76(6): 425-440, 2010. PubMed
- [3] Doi, K. et al., Evaluation of new acute kidney injury biomarkers in a mixed intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 39(11): 2464-2469, 2011. PubMed