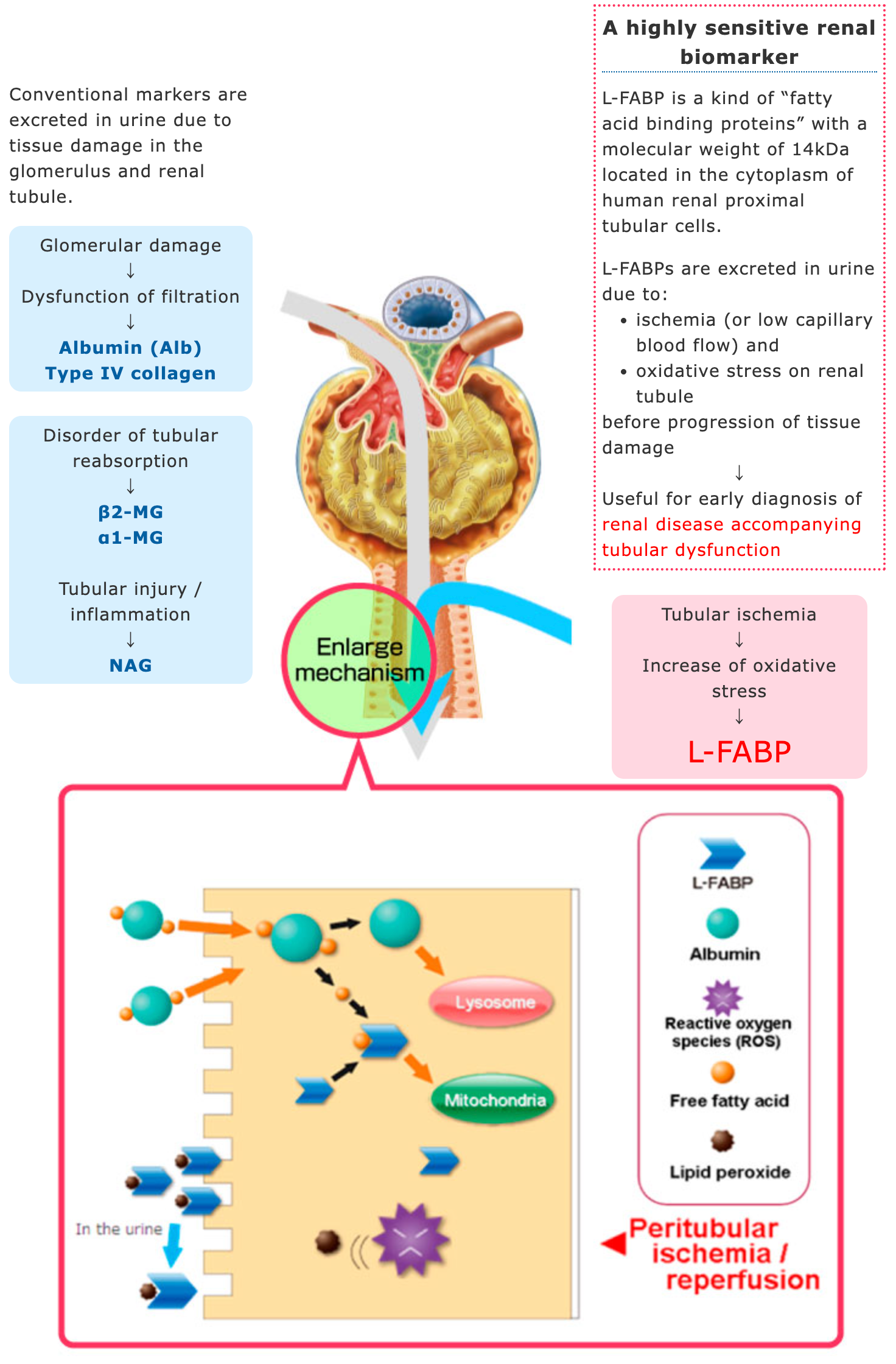
Schematic diagram of glomerulus and renal tubule
Product information
Clinical Utilities
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
- To diagnose severity and treatment effects of sepsis patients
- To predict AKI outbreak after cardio-vascular surgery
- To determine in ICU patients the high risk of developing sever Acute Kidney Injury
- To predict onset of CIN AKI
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- To diagnose diabetic nephropathy in early stage
- To diagnose in early stage of renal disease accompanying tubular dysfunction
- To identify the risk of diabetic nephropathy progress in early stage
- For the determination of microcirculation disorder (ischemia)
- To differentiate focal glomerulosclerosis and minor glomerular abnormalities