【CKD】To differentiate focal glomerulosclerosis and minor glomerular abnormalities
The comparison between biomarkers in patients with focal glomerulosclerosis and with minor glomerular abnormalities
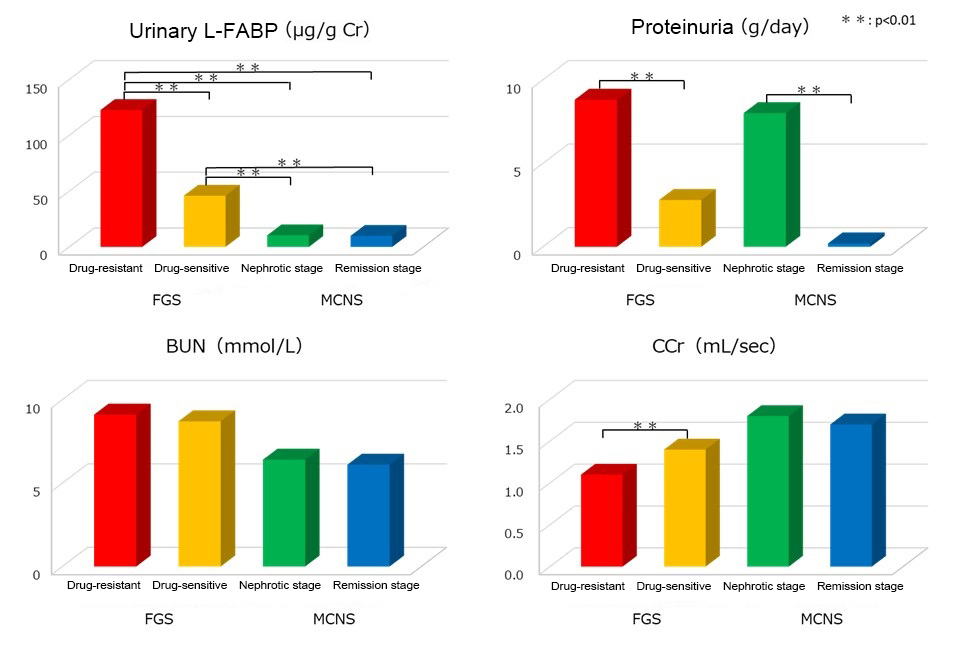 Table 1 and 2 from Nakamura, T. et al., Clin Nephrol. 65(1), 2006.[1]
Table 1 and 2 from Nakamura, T. et al., Clin Nephrol. 65(1), 2006.[1]
DATA
- Method
- Urinary L-FABP, protein and BUN levels and creatinine clearance of 17 patients with focal glomerulosclerosis (8 with drug-resistant and 9 with drug-sensitive) and 24 patients with minor glomerular abnormalities (14 in nephrotic stage and 10 in remission stage) were measured and compared.
*Prednisolone is administered to patients with focal glomerulosclerosis for 6 months and patients who have treatment effect classified as drug-sensitive and who do not have as drug-resistant.
- Results
- Compared to patients with minor glomerular abnormalities, the urinary L-FABP level is significantly higher in patients with focal glomerulosclerosis, furthermore among patients with focal glomerulosclerosis, urinary L-FABP level is significantly higher in drug-resistant patient compared to drug-sensitive patients. There is no significant difference in urinary protein and BUN levels and creatinine clearance in both patient groups. The diagnosis of focal glomerulosclerosis and minor glomerular abnormalities which are difficult to distinguish but the determination is possible from urinary L-FABP measurement.
The change in each biomarker with LDL apheresis in drug-resistant focal glomerulosclerosis patitents
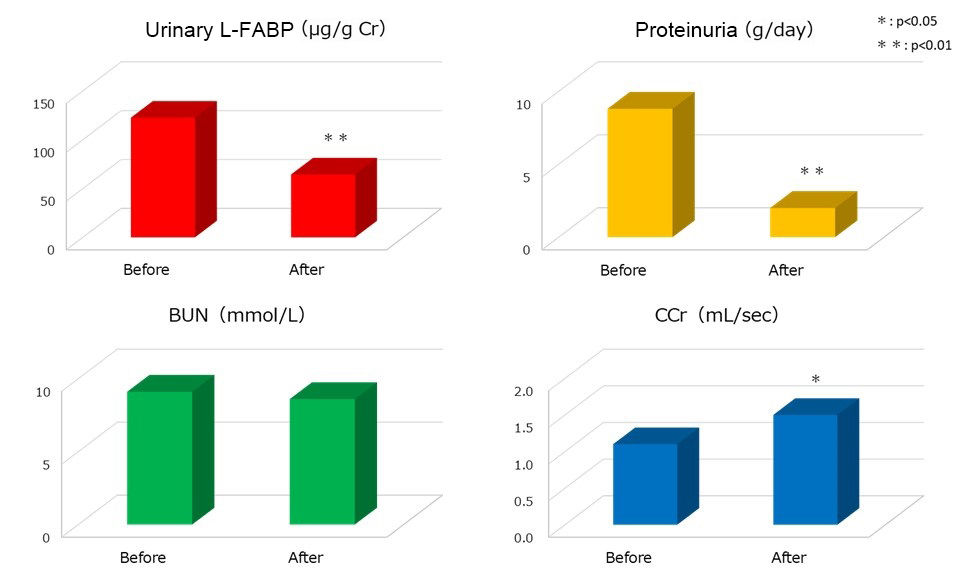 Table 4 from Nakamura, T. et al., Clin Nephrol. 65(1), 2006.[1]
Table 4 from Nakamura, T. et al., Clin Nephrol. 65(1), 2006.[1]
DATA
- Method
- LDL apheresis which remove LDL from patient’s blood, was performed to 8 drug-resistant patients with focal glomerulosclerosis and urinary L-FABP, protein and BUN levels and creatinine clearance are measured and compared.
- Results
- Urinary L-FABP and protein levels were significantly decreased and creatinine clearance was significantly increased with LDL apheresis effect. LDL apheresis ameliorates tubulointerstitial disease and urinary L-FABP is helpful indicator for its amelioration effect.
Reference
- [1] Nakamura, T. et al., Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein levels for differential diagnosis of idiopathic focal glomerulosclerosis and minor glomerular abnormalities and effect of low-density lipoprotein apheresis. Clin Nephrol. 65(1), 2006.PubMed

